
Personnel: Mohamad Zubair
Research Investigator
(Member of the Hammer Lab Since September 2008)
Academic Appointments
| 2008-present | Research Investigator, Medical School University of Michigan, MI |
| 2007-2008 | Research Scientist, UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, Tx |
| 2005-2007 | Research Specialist, NIBB Okazaki Japan |
Education
| 2000-2007 | Postdoctoral National Institute for Basic Biology (NIBB), Okazaki Japan Supervisor: Ken-ichirou Morohashi, Prof., Ph.D. |
| 1998-2000 | Postdoctoral National Institute for Basic Biology (NIBB), Okazaki Japan Supervisor: Masaharu Noda, Prof., Ph.D. |
| 1998 | Ph.D. Kyushu University, Fukuoka Japan |
| 1993 | M.S. Kyushu University, Fukuoka Japan |
| 1991 | B.S. Meijo University, Nagoya Japan |
Investigation of the Key Factor in Adrenal Development
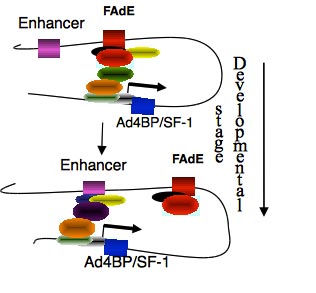
The mouse adrenal gland develops from cells of the coelomic epithelium and mesonephos that migrate and expand to form the adrenogonadal primordium, which separates at about e10.5 to form the gonadal primordiun and adrenal primordium. At about e 11.5-12.5 a mesenchymal capsule forms around the fetal adrenal cortex and neural crest cell migrate in to form the adrenal medulla. Loss of function studies have shown that the nuclear receptor, Steroidogenic Factor 1 (Ad4BP/SF1-/Nr5A1) is essential for adrenal development. Recently, Fetal Adrenal specific Enhancer (FAdE) of the Ad4BP/SF-1 gene was identified as the region responsible for regulated expression of SF-1 in the transient fetal zone (1). From the later fetal stages to puberty, cells of the adult or definitive zone increase in number, whereas those of the fetal zone decrease in number and accumulate at the boundary of the cortex and medulla. Thereafter, the fetal zone, originally termed the X zone in histological studies in mice, gradually disappeared. The lineage tracing studies establish definitively that the adult cortex derives from precursor cells in the fetal cortex in which the FAdE was activated before the organization into two distinct zones (2). The potential of these fetal adrenocortical cells to enter a pathway to derive cells of the adult cortex disappeared by E14.5 of mouse embryo days. However, the precise developmental relationship between the fetal and adult zones is poorly understood. For example, as the FAdE is no longer active, how do these cells maintain Sf1 expression while their cell types change during organogenesis? Since tissue-specific enhancers are key determinants of tissue-specific gene expression, study of enhancer function should provide important insights into the mechanisms underlying tissue development. Ongoing investigations in Dr. Hammer’s lab are aimed at identifying the Ad4BP/SF-1 enhancer responsible for Ad4BP/SF-1 expression in the definitive adult adrenal (DAdE). Identification of the definitive/adult enhancer is critical for our understanding of adrenal gland development, cell fate transition events and potentially of errors in regulation that result in adrenal disease.
References:
- Zubair, M., Ishihara, S., Oka, S., Okumura, K. and Morohashi, K. (2006) Two-step regulation of Ad4BP/SF-1 gene transcription during fetal adrenal development: initiation by a Hox-Pbx1-Prep1 complex and maintenance via autoregulation by Ad4BP/SF-1. Mol Cell Biol 26, 4111-21.
- Zubair, M., Parker, K.L. and Morohashi, K. (2008) Developmental links between the fetal and adult zones of the adrenal cortex revealed by lineage tracing. Mol Cell Biol 28, 7030-40.
Expression of Ad4BP/SF-1 is driven by diverse enhancers during adrenal developmental stages. Our previous result revealed that FAdE drives Ad4BP/SF-1 expression at earlier stage of fetal adrenal. But this function will be repressed while cells differentiate into adult type. This suggested that another unidentified adult adrenal enhancer drives the gene expression in these later developmental stages.
Recent Publications
- Morohashi K, and Zubair M: The fetal and adult adrenal cortex. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2010.
- MZubair M, Oka S, Parker KL, Morohashi K: Transgenic expression of Ad4BP/SF-1 in fetal adrenal progenitor cells leads to ectopic adrenal formation. Mol Endocrinol 2009, 10:1657-1667.
- MZubair M, Parker KL, Morohashi K: Developmental links between the fetal and adult zones of the adrenal cortex revealed by lineage tracing. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28:7030-7040.
- MShima Y, Zubair M, Komatsu T, Oka S, Yokoyama C, Tachibana T, Hjalt TA, Drouin J, Morohashi K: Pituitary homeobox 2 regulates adrenal4 binding protein/steroidogenic factor-1 gene transcription in the pituitary gonadotrope through interaction with the intronic enhancer. Mol Endocrinol 2008, 22:1633-1646.
- MSato Y, Baba T, Zubair M, Miyabayashi K, Toyama Y, Maekawa M, Owaki A, Mizusaki H, Sawamura T, Toshimori K, Morohashi K, Katoh-Fukui Y: Importance of forkhead transcription factor Fkhl18 for development of testicular vasculature. Mol Reprod Dev 2008, 75:1361-1371.
Curriculum Vitae
Please click here to view my full curriculum vitae.





